Understanding why and how researchers and innovators make data access requests
The Gateway contains over 500 datasets (and growing) that are discoverable using the Gateway’s easy-to-use interface. And a primary objective of the Gateway is to simplify, streamline and therefore reduce the time it takes users to submit, and data custodians to review and make a decision on user requests for access to data.
Now that data is discoverable on the Innovation Gateway, the next step is to understand where it will support their work, and how they will request access to it. This is where the Data Access Request (DAR) functionality of the Gateway comes into play.
A DAR is the process by which a user can make contact with a data custodian to request access to their data. Their request is supported by additional information about the work they want to use the data to support.
How applicants can request access - Video tutorial: How to submit a data access request
Before applicants can request access, they first need to find a dataset that suits their research needs. They will also need a Gateway user account and must be logged in to the make an application.
- Applicants will see a Request access button if you are a custodian using the short enquiry form
- Applicants will see a How to request access button if you are a custodian using the new 5 safes application form.
- Applicants are encouraged to send a message to the custodian before starting the application process.
Data Access Request (DAR) Forms
Depending on the custodian, users will either be able to send a data request enquiry to the custodian (Short Form Data Access Request) or, where a Data Custodian has implemented a 5 safes DAR Form on the Gateway (Long form Data Access Request), the entire DAR process can be conducted electronically through the Gateway itself. The 5 safes process offers other supportive functionality to both data requesters and custodians by enabling secure communications between requestor and data custodian in advance of submitting a DAR; powerful collaboration tools to allow collaborators to work together to complete the DAR, and the ability to monitor DAR progress.
Short form Data Access Requests
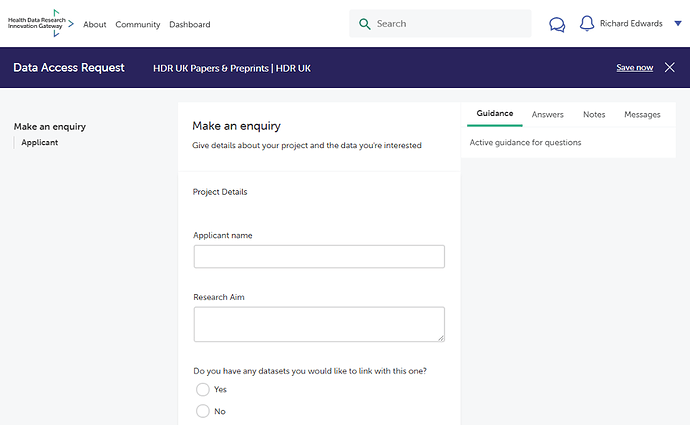
Unless a Data Custodian has been onboarded to the 5 safes DAR process, all data requests will be handled through a simple enquiry form. An example of this is set out in the figure below.
The enquiry screen captures key information about the user’s project and the data that they are interested in. It includes:
- Applicant name
- Research aim
- Whether there is a requirement to link datasets
- Which parts of the dataset the user is interested in
- Proposed project start date
- ICO number
- Research benefits (optional field)
- Ethical processing evidence (optional field)
- Contact telephone number (optional field)
Once the user has completed and submitted the enquiry form, the content of this will be emailed to the data custodian for consideration. For these types of enquiry there are no other steps that need to be undertaken on the Gateway.
Long form Data Access Requests
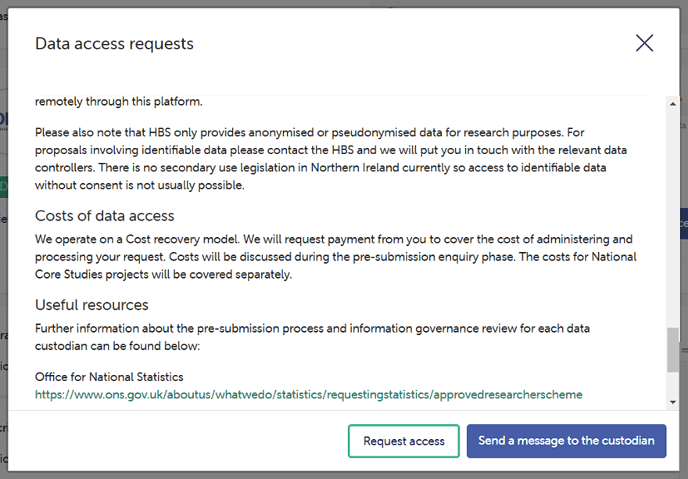
Where a Data Custodian has onboarded to the 5 safes DAR process, a much more advanced and fully featured set of DAR functionality is available to the custodian. In the majority of cases, this allows the custodian to process the entire DAR electronically through the Gateway, helping avoid onerous and time consuming fragmented and/or paper based processes.
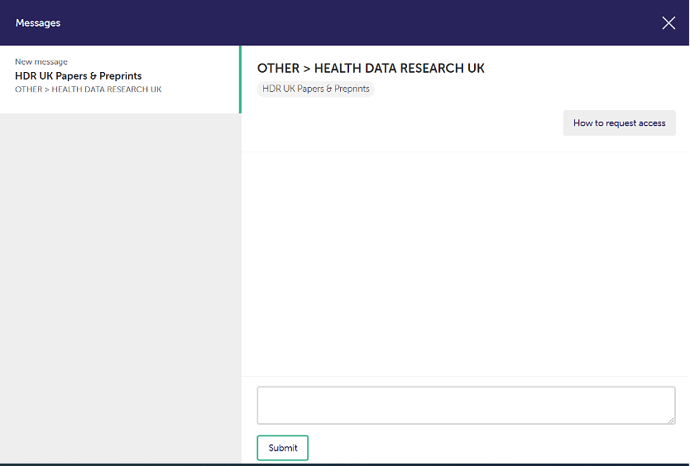
As illustrated in the images above and below, where a 5 safes DAR has been implemented, should they have any questions, users have the ability to message the custodian prior to submitting the application. This messaging function exists entirely within the Gateway application, is specific to each data request, and therefore is much simpler for custodians to administer compared to other tools such as email.
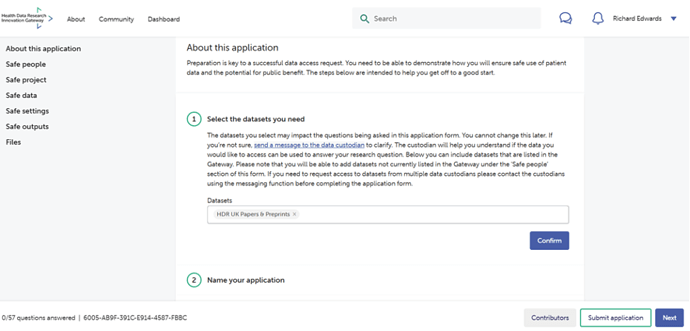
Once a user decides to submit a 5 safes DAR, they are required to select one or more datasets that they would like access to. Working with other contributors if relevant, the user(s) are then required to answer questions across each of the 5 domains of Safe people, Safe project, Safe data, Safe settings, and Safe outputs. This is illustrated in the image below.
Once the user(s) has completed and submitted the application the custodian is then able to review the application, query aspects of it and/or ask for further information and then decide on whether to approve the application (with or without conditions) or reject it. All of this can be done through the Gateway.